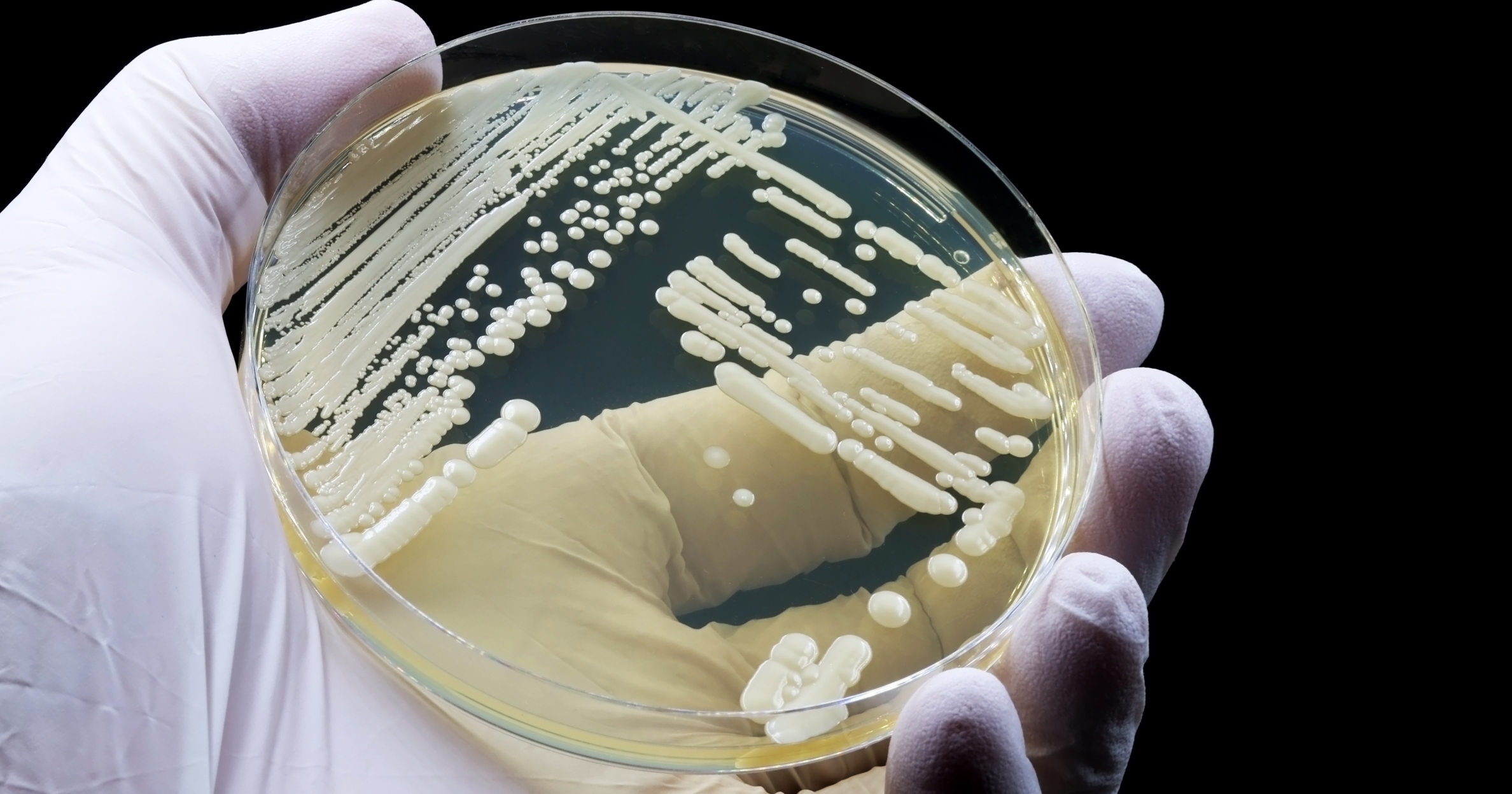
Candida aurisa fungus first identified in Japan in 2009, has been rampant in the United States, with at least 7,000 infections reported in 27 states by 2025, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). This increase has resulted in broader recognition of its virulence and resistance to conventional treatments.
A recent study from the Hackensack Meridian Center for Discovery and Innovation, published in Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviewshas revealed that the dense structure of the cell wall of Candida auris contributes to its notable drug resistance.
This fungus has evolved to evade host interactions, making it a significant threat, especially to people with compromised immune systems.
Diagnosis and treatment
Laboratory tests to identify Candida auris have proven complicated, often leading to erroneous results due to confusion with other yeasts. Although four classes of antifungal medications are available, their effectiveness varies.
Three new drugs are currently in clinical trials, raising hopes for better treatment options in the future.
Prevention strategies
Researchers emphasize the need to develop new antifungal agents and improve diagnostic tests. “Taken together, these data underscore the need to develop new antifungal agents with broad-spectrum activity against human pathogenic fungi, improve diagnostic testing, and develop complementary immune-based modalities and vaccines for the treatment of high-risk patients,” the researchers said in a joint statement reported by Newsweek.
Furthermore, the importance of creating more effective surveillance mechanisms, especially in countries with limited resources, to manage and improve the outcomes of patients affected by opportunistic fungal infections is highlighted.
Symptoms of Candida auris infection
The most common symptoms of an infection Candida auris They include high fever and chills that do not improve with antibiotics.
General symptoms. The Candida auris It causes serious infections, especially in the bloodstream, with signs such as fatigue, dizziness, increased heart rate and vomiting. These symptoms are similar to other fungal or bacterial infections, which complicates their identification in already hospitalized patients.
Symptoms by location. Depending on the affected site, wound, ear or urinary infections may appear, with persistent fever and low blood pressure in severe cases. In immunocompromised patients, the infection spreads rapidly without noticeable specific symptoms at the onset.
Risk factors
The main risk factors for contracting infections Candida auris They are related to hospital environments and conditions of medical vulnerability.
Hospital factors. Prolonged hospitalizations, stays in nursing homes, and contact with contaminated surfaces increase the risk of colonization and infection by Candida aurissince this fungus persists in the environment and is easily transmitted. The presence of invasive devices such as central venous catheters, mechanical ventilation tubes and urinary catheters facilitates the entry of the pathogen.
Medical conditions. Patients with immunosuppression, multiple comorbidities (such as diabetes or cancer), recent surgeries or prolonged use of broad-spectrum antibiotics and antifungals have greater susceptibility. Previous skin colonization, detected in the armpits, groin or rectum, increases the probability of invasive infection in these groups.
You may also be interested in:
